Toluene and xylene are both aromatic hydrocarbons that are commonly used as solvents and are produced from crude oil. While they share some similarities, there are also differences in their functions and properties:
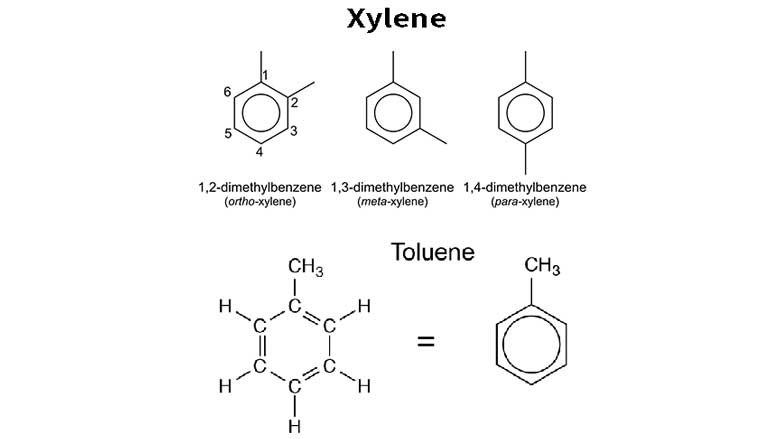
- 1. Chemical Structure: Toluene (C7H8) has a benzene ring with a methyl group attached, while xylene (C8H10) has a benzene ring with two methyl groups attached at different positions.
- 2. Solvent Properties: Both toluene and xylene are effective solvents for a wide range of materials, including paints, lacquers, adhesives, and coatings. However, xylene is often considered a more powerful solvent compared to toluene. Xylene is commonly used in applications that require stronger solvency, such as in the printing, rubber, and leather industries.
- 3. Applications: Toluene is widely used in the production of gasoline additives, explosives, synthetic fibers, and pharmaceuticals. It is also used as a solvent in paints, coatings, and adhesives. Xylene, on the other hand, is commonly used in the production of polyester fibers, dyes, and coatings. It is also used as a cleaning agent in the electronics industry and as a solvent in the manufacture of rubber, leather, and printing inks.
- 4. Isomer Composition: Xylene exists in three isomeric forms: ortho-xylene, meta-xylene, and para-xylene. These isomers have slightly different chemical properties and are used in different applications. Toluene does not have isomers.
- 5. Toxicity: Both toluene and xylene are toxic and can cause health problems.




